except KeyboardInterrupt
Since Ctrl-C causes KeyboardInterrupt to be raised, just catch it outside the loop and ignore it.
kinkun's blog
except KeyboardInterrupt
Since Ctrl-C causes KeyboardInterrupt to be raised, just catch it outside the loop and ignore it.
KyeboardからWhile LoopでEvent作成
def sample1(value):
print(value)
try:
while True:
value = input()
sample1(value)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
pass結果
9
9
0
0Kyeboard入力とFunctionの使い方
def sample1(value):
print(value)
value = input()
sample1(value)結果
9
9function呼び出し
def sample1(a, b, c):
s = a + b - c
print(a)
if a == 0:
print(b)
else:
print(c)
sample1(1, 1, 2)結果
1
2Pythonインストールと動作確認
・インストール
Windowsの場合、以下のURLにて、インストーラをダウンロードします。
https://www.python.org/downloads/windows/
・ダウンロードしたインストーラをPCにインストールします。
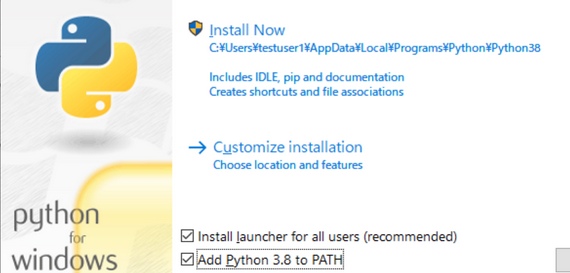
※インストール時、注意事項として、以下のように箇所にチェックいれて、「Install Now」押下します。
・インストール後に、PCの中に「test.py」ファイル作成して、その中に、以下のコードを入力して、保存します。
print("Hello world!")保存場所は、例えば、C:\Python\test.py
・Python Versionを確認します。
Windowsの場合、コマンドプロンプトを起動して、まずPythonを確認します。
C:\Users\p445-PC>python --version
Python 3.11.1・作成した、test.pyを実行します。
test.pyが保存されているDirectoryに移動します。
C:\>cd Pythontest.py実行します。
C:\Python>python test.py
Hello world!Apexテストクラスのエラー「TestMethod として定義されたメソッドは、getContent コールをサポートしていません。」対応
attachmentFile.Body = Test.isRunningTest() ? Blob.valueof('testString') : pr.getContent();Apex StandardControllerテストクラス
@isTest
private class Test_testController {
static testmethod void test1() {
Account acc = new Account(
Name='テスト'
);
insert acc;
Test.startTest();
ApexPages.StandardController sc = new ApexPages.StandardController(acc);
testController testSC = new testController(sc);
PageReference pageRef = Page.testPage;
pageRef.getParameters().put('id', String.valueOf(acc.Id));
Test.setCurrentPage(pageRef);
testSC.testMethod();
Test.stopTest();
}
}項目一括作成
シナリオとして、取引先のカスタム項目をカスタムオブジェクトに一括コピーする。
手順
・組織のソースファイルを持ったvscodeのターミナルに下記コードを入力して実行する。実装すると、ソースファイルがメタデータに変換され、メタデータのフォルダとその下にファイルが新たに作成される。
sfdx force:source:convert
・作成したメタデータのコードをコピーして、作成したいカスタム項目のコードを追加する。
・ターミナルに下記コードを入力したら実行してメタデータをソースファイルに再変換する。
sfdx force:mdapi:convert -r メタデータフォルダパス
例えば、
sfdx force:mdapi:convert -r metadataPackage_1234567890123
・対象のファイルをデプロイすると、環境にカスタム項目が一括で作成される。
ただ、別途項目レベルセキュリティの設定が必要である。
SetのaddAllメソッド
Set<String> myString = new Set<String>{'a', 'b'};
Set<String> sString = new Set<String>{'c'};
Boolean result1 = myString.addAll(sString);
system.debug('myString:'+myString);
System.assertEquals(true, result1);結果
myString:{a, b, c}半角英数字のみ許可する入力規則
NOT( REGEX( test__c , "^[0-9a-zA-Z]*$") )